Working principle of Cold room chamber screw compressor and comparison of fully enclosed, semi-closed and open type
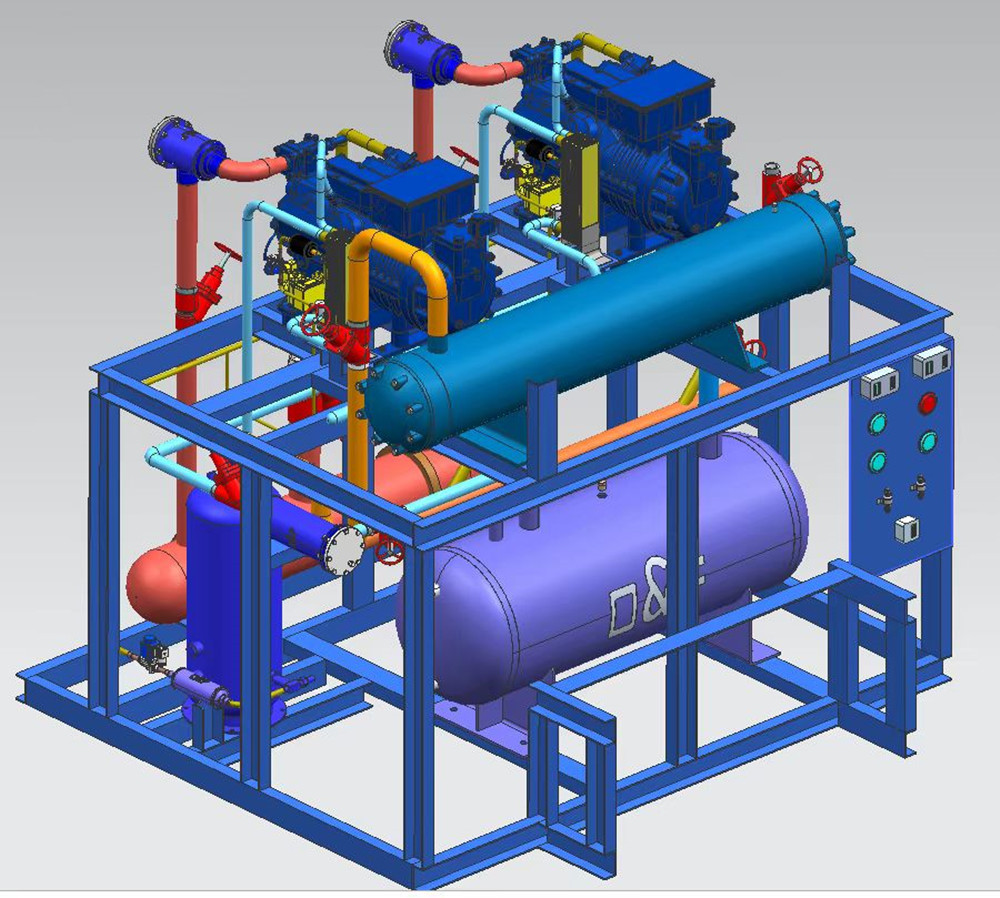
The working principle and structure of cooling room screw compressor:
1. Inhalation process: The air intake port of the screw type must be designed so that the compression chamber can fully inhale, while the freezing room screw air compressor does not have an intake and exhaust valve group, and the air intake only relies on a regulating valve When the rotor rotates, the tooth groove space of the main and auxiliary rotors is the largest when it turns to the opening of the air inlet end wall. At this time, the tooth groove space of the rotor is communicated with the free air of the air inlet for the cold storage. When exhausting, the air in the tooth groove is completely discharged. When the exhaust is finished, the tooth groove is in a vacuum state. When it is turned to the air inlet, the outside air is sucked in and flows into the tooth groove of the main and auxiliary rotors in the axial direction. Blast freezer Screw air compressor maintenance reminder When the air fills the entire tooth groove, the end face of the intake side of the rotor turns away from the air inlet of the casing, and the air between the tooth grooves is closed.
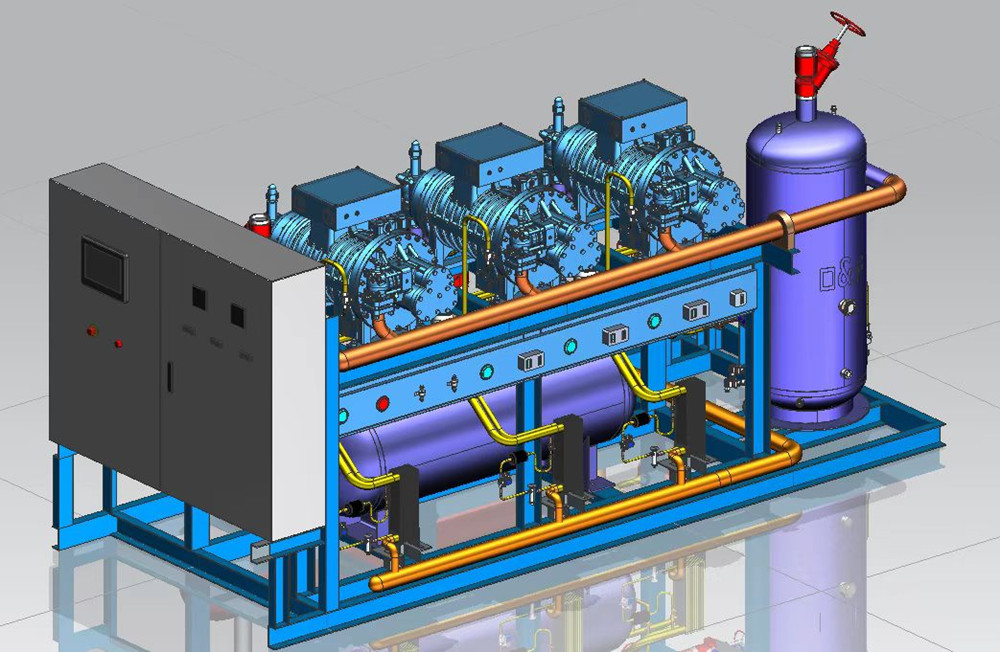
2. Sealing and conveying process: When the main and auxiliary rotors are inhaled, the tooth peaks of the main and auxiliary rotors are closed with the casing. At this time, the air is closed in the tooth groove and no longer flows out, that is, [sealing process]. The two rotors continue to rotate, their tooth peaks and tooth grooves match at the suction end, and the matching surface gradually moves to the discharge end.
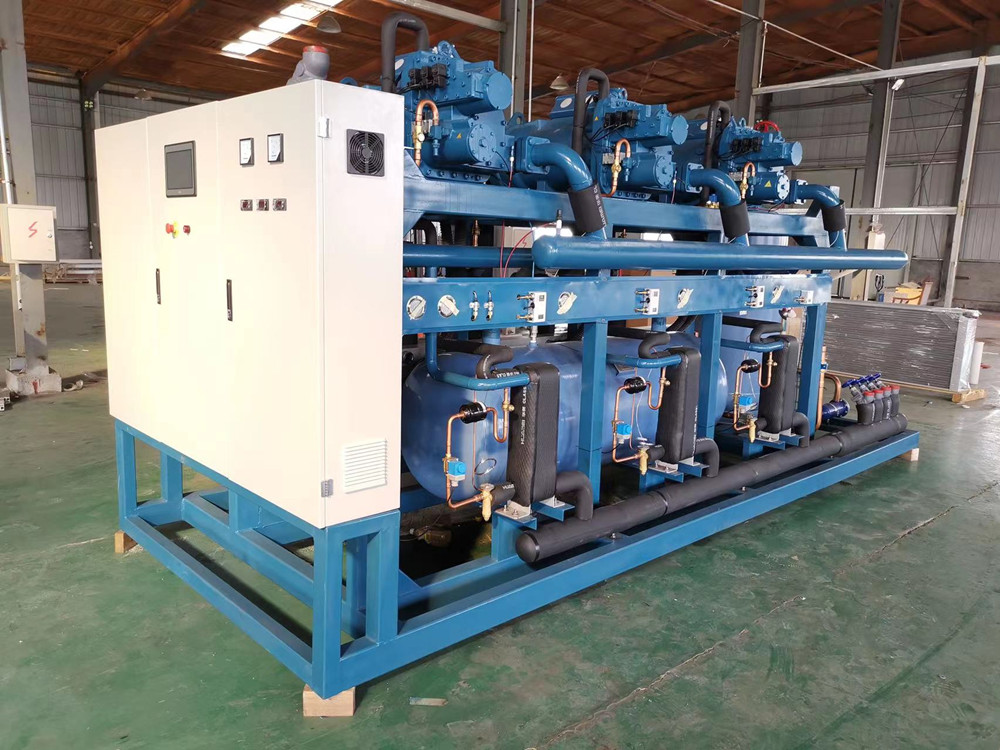

3. Compression and fuel injection process: During the conveying process, the meshing surface gradually moves to the exhaust end, that is, the gap between the meshing surface and the exhaust port gradually decreases, the gas in the tooth groove is gradually compressed, and the pressure increases. , which is the [compression process]. At the same time of compression, the lubricating oil is also injected into the compression chamber and mixed with the chamber air due to the action of the pressure difference.
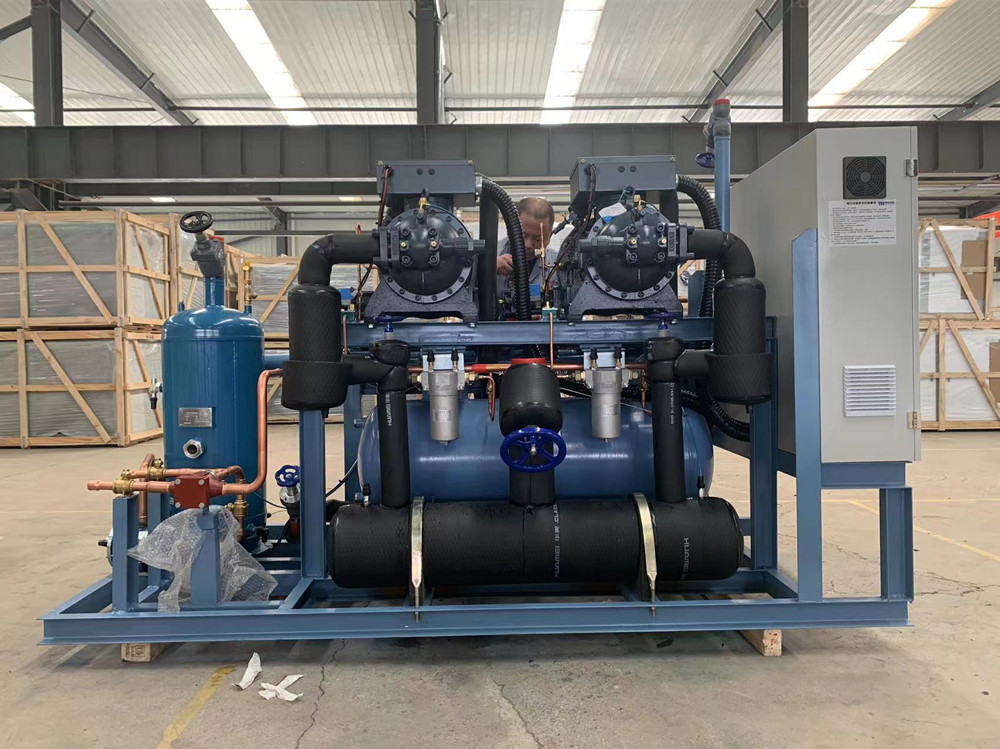

4. Exhaust process: when the meshing end face of the rotor turns to communicate with the exhaust of the casing during the maintenance of the screw air compressor, (at this time the pressure of the compressed gas is the highest) the compressed gas begins to be discharged, until the peaks and grooves of the teeth meet. The meshing surface is moved to the exhaust end face. At this time, the space between the meshing surfaces of the two rotors and the exhaust port of the casing is zero, that is, the exhaust process is completed. The groove length reaches the longest again, and its inhalation process is going on again.

